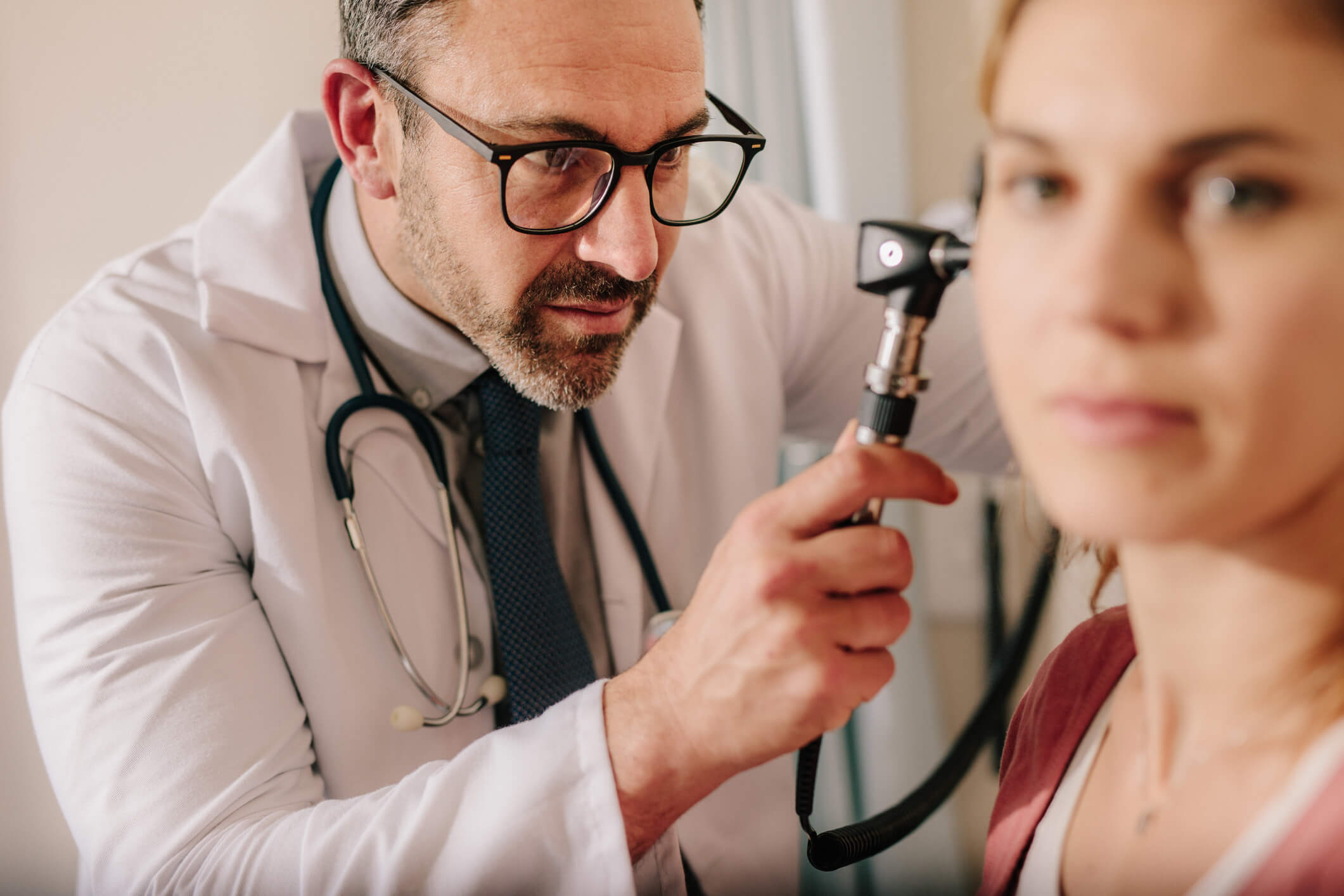

Chronic Ear Infections
Ear infections are a common condition that usually go away within a few days with minor treatments. Chronic ear infections, however, do not heal on their own and may need specialized treatment in order to go away. These are often caused when the eustachian tube, which is the tube that drains fluid away from the middle ear, becomes clogged. The buildup of fluid causes pressure on the eardrum.
What Are the Symptoms of Ear Infections?
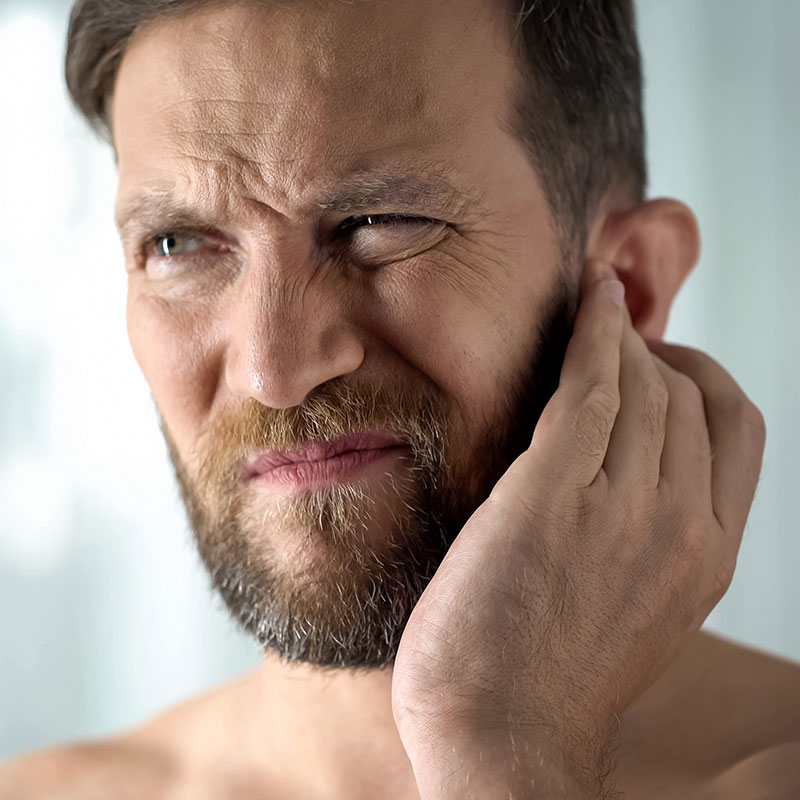
Middle Ear Infection
Ear Infections and a Perforated Eardrum
Swimmer’s Ear
Will I Get My Hearing Back After an Ear Infection?
Recurring Ear Infections and Long-Term Hearing Loss
If you’re suffering from chronic ear infections, we can help. Call Us